Suunto 5 User guide
Intensity zones
Using intensity zones for exercising helps guide your fitness development. Each intensity zone stresses your body in different ways, leading to different effects on your physical fitness. There are five different zones, numbered 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest), defined as percentage ranges based on your maximum heart rate (max HR), pace or power.
It is important to train with intensity in mind and understand how that intensity should feel. And don't forget, regardless of your planned training, that you should always take time to warm up before an exercise.
The five different intensity zones used in Suunto 5 are:
Zone 1: Easy
Exercising in zone 1 is relatively easy on your body. When it comes to fitness training, intensity this low is significant mainly in restorative training and improving your basic fitness when you are just beginning to exercise, or after a long break. Everyday exercise – walking, climbing stairs, cycling to work, etc. – is usually performed within this intensity zone.
Zone 2: Moderate
Exercising at zone 2 improves your basic fitness level effectively. Exercising at this intensity feels easy, but workouts with a long duration can have a very high training effect. The majority of cardiovascular conditioning training should be performed within this zone. Improving basic fitness builds a foundation for other exercise and prepares your system for more energetic activity. Long duration workouts at this zone consume a lot of energy, especially from your body’s stored fat.
Zone 3: Hard
Exercising at zone 3 begins to be quite energetic and feels like pretty hard going. It will improve your ability to move quickly and economically. In this zone, lactic acid begins to form in your system, but your body is still able to completely flush it out. You should train at this intensity at most a couple of times per week, as it puts your body under a lot of stress.
Zone 4: Very hard
Exercising at zone 4 will prepare your system for competition type events and high speeds. Workouts in this zone can be performed either at constant speed or as interval training (combinations of shorter training phases with intermittent breaks). High-intensity training develops your fitness level quickly and effectively, but done too often or at too high intensity may lead to overtraining, which may force you to take a long break from your training program.
Zone 5: Maximal
When your heart rate during a workout reaches zone 5, the training will feel extremely hard. Lactic acid will build up in your system much faster than it can be removed, and you will be forced to stop after a few minutes at most. Athletes include these maximum-intensity workouts in their training program in a very controlled manner, fitness enthusiasts do not require them at all.
Heart rate zones
Heart rate zones are defined as percentage ranges based on your maximum heart rate (max HR).
By default, your max HR is calculated using the standard equation: 220 - your age. If you know your exact max HR, you should adjust the default value accordingly.
Suunto 5 has default and activity-specific HR zones. The default zones can be used for all activities, but for more advanced training, you can use specific HR zones for running and cycling activities.
Set max HR
Set your maximum HR from the settings under Training » Intensity zones » Default zones.
- Select the max HR (highest value, bpm) and press the middle button.
- Select your new max HR by pressing the upper right or lower right buttons.
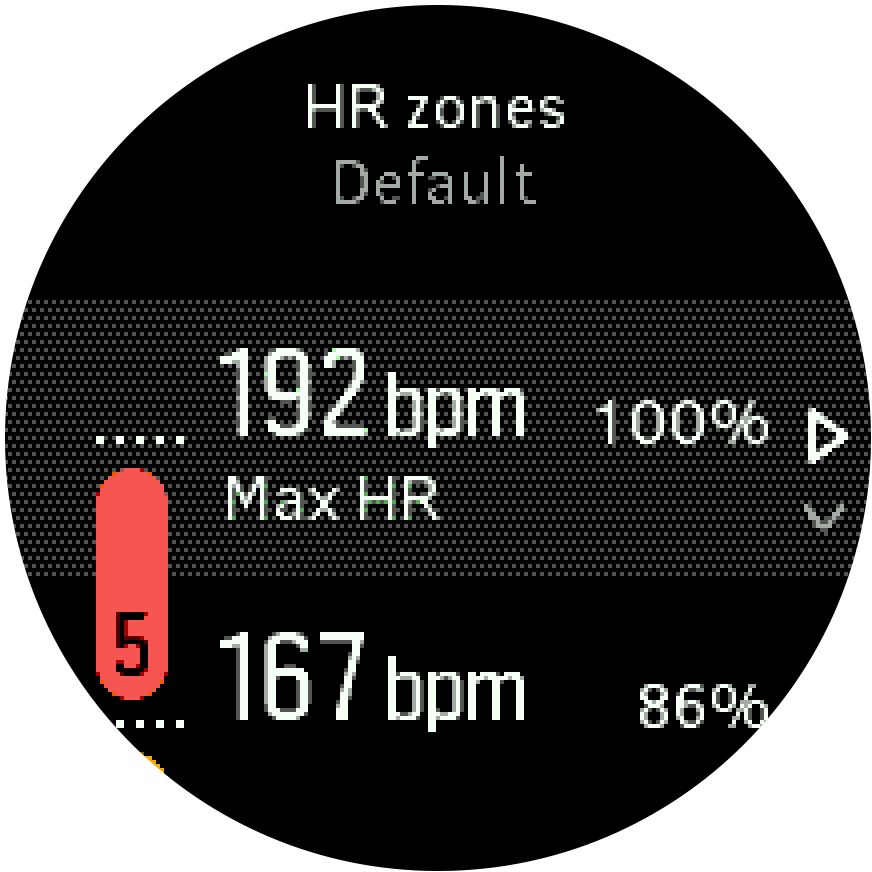
- Press the middle button to select the new max HR.
- Keep the middle button pressed to exit the HR zones view.
You can also set your maximum HR from the settings under General » Personal.
Set default HR zones
Set your default HR zones from the settings under Training » Intensity zones » Default zones.
- Scroll up/down by pressing the upper right or lower right buttons and press the middle button when the HR zone you want to change is highlighted.
- Select your new HR zone by pressing the upper right or lower right buttons.
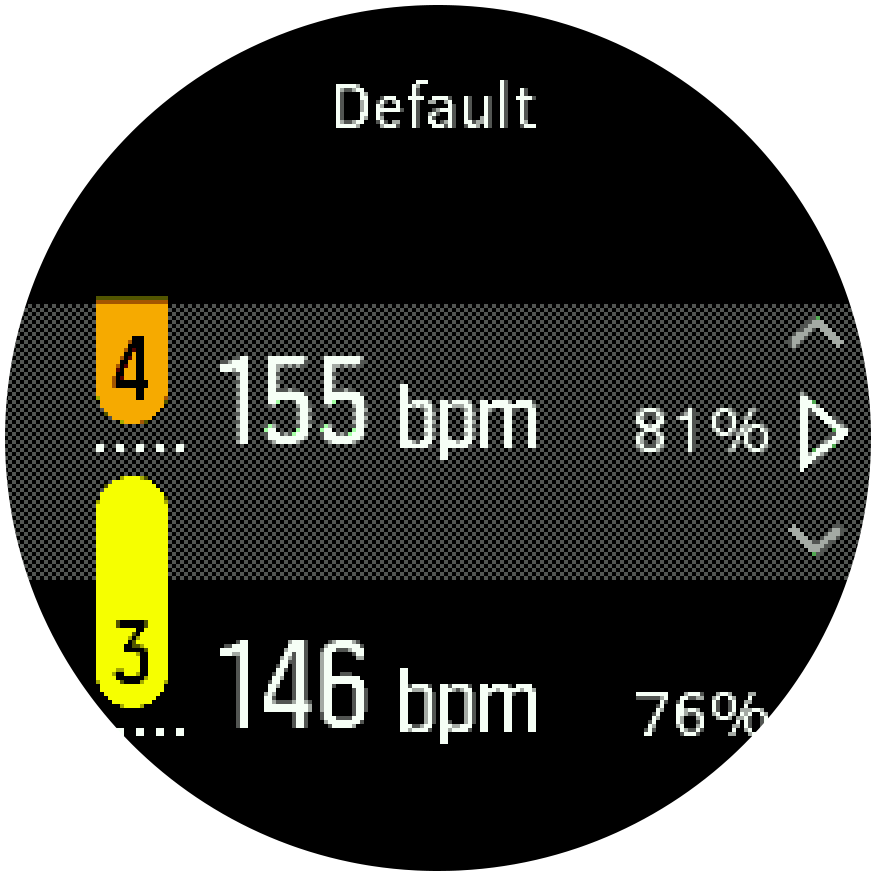
- Press the middle button to select the new HR value.
- Keep the middle button pressed to exit the HR zones view.
Selecting Reset in the HR zones view will reset the HR zones to the default value.
Set activity specific HR zones
Set your activity specific HR zones from the settings under Training » Intensity zones » Advanced zones.
- Choose the activity (running or cycling) that you want to edit (by pressing upper right or lower right buttons) and press the middle button when the activity is highlighted.
- Press the middle button to toggle the HR zones on.
- Scroll up/down by pressing the upper right or lower right buttons and press the middle button when the HR zone you want to change is highlighted.
- Select your new HR zone by pressing the upper right or lower right buttons.
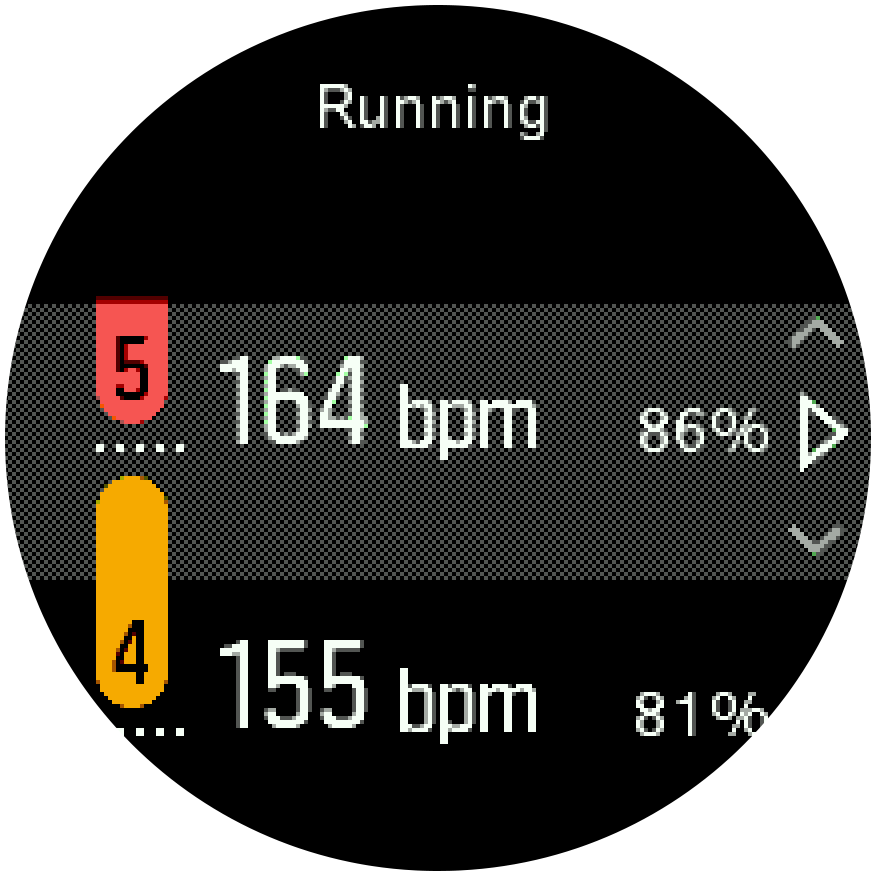
- Press the middle button to select the new HR value.
- Keep the middle button pressed to exit the HR zones view.
Using HR zones when exercising
When you record an exercise (see Recording an exercise), and have selected heart rate as an intensity target (see Using targets when exercising), an HR zone gauge, divided into five sections, is shown around the outer edge of the sport mode display (for all sport modes that support HR). The gauge indicates in which HR zone you are currently training by lighting up the corresponding section. The small arrow in the gauge indicates where you are within the zone range.

Your watch alerts you when you hit your selected target zone. During your exercise the watch will prompt you to speed up or slow down, if your heart rate is outside the selected target zone.

In the exercise summary, you get a breakdown of how much time you have spent in each zone.
Pace zones
Pace zones work just like HR zones but the intensity of your training is based on your pace instead of your heart rate. The pace zones are shown either as metric or imperial value depending on your settings.
Suunto 5 has five default pace zones that you can use or you can define your own.
Pace zones are available for running.
Set pace zones
Set your activity specific pace zones from the settings under Training » Intensity zones » Advanced zones.
- Select Running by pressing the middle button.
- Press the lower right button and select pace zones.
- Press the upper right or lower right buttons to scroll and press the middle button when the pace zone you want to change is highlighted.
Select your new pace zone by pressing the upper or lower buttons.

Press the middle button to select the new pace zone value.
- Press and hold the middle button to exit the pace zones view.
Using pace zones when exercising
When you record an exercise (see Recording an exercise), and have selected pace as an intensity target (see Using targets when exercising) a pace zone gauge, divided into five sections, is viewed. These five sections are shown around the outer edge of the sport mode display. The gauge indicates the pace zone you have chosen as an intensity target by lighting up the corresponding section. The small arrow in the gauge indicates where you are within the zone range.

Your watch alerts you when you hit your selected target zone. During your exercise the watch will prompt you to speed up or slow down, if your pace is outside the selected target zone.

In the exercise summary, you get a breakdown of how much time you have spent in each zone.
Power zones
Power meter measures the amount of physical effort needed to perform a certain activity. The effort is measured in watts. The main advantage gained with a power meter is precision. The power meter reveals exactly how hard you really work and how much power you produce. It is also easy to see your progress when analyzing the watts.
Power zones can help you train with the correct power output.
Suunto 5 has five default power zones that you can use or you can define your own.
Power zones are available in all default sport modes for cycling, indoor cycling and mountain biking. For running and trail running, you need to use the specific “Power” sport modes to get power zones. If you are using custom sport modes, make sure your mode uses a power POD so that you also get power zones.
Set activity specific power zones
Set your activity specific power zones from the settings under Training » Intensity zones » Advanced zones.
- Select the activity (Running or Cycling) that you want to edit or press the middle button when the activity is highlighted.
- Press the lower right button and select power zones.
- Press the upper right or lower right buttons and select the power zone you want to edit.
Select your new power zone by pressing the upper or lower buttons.
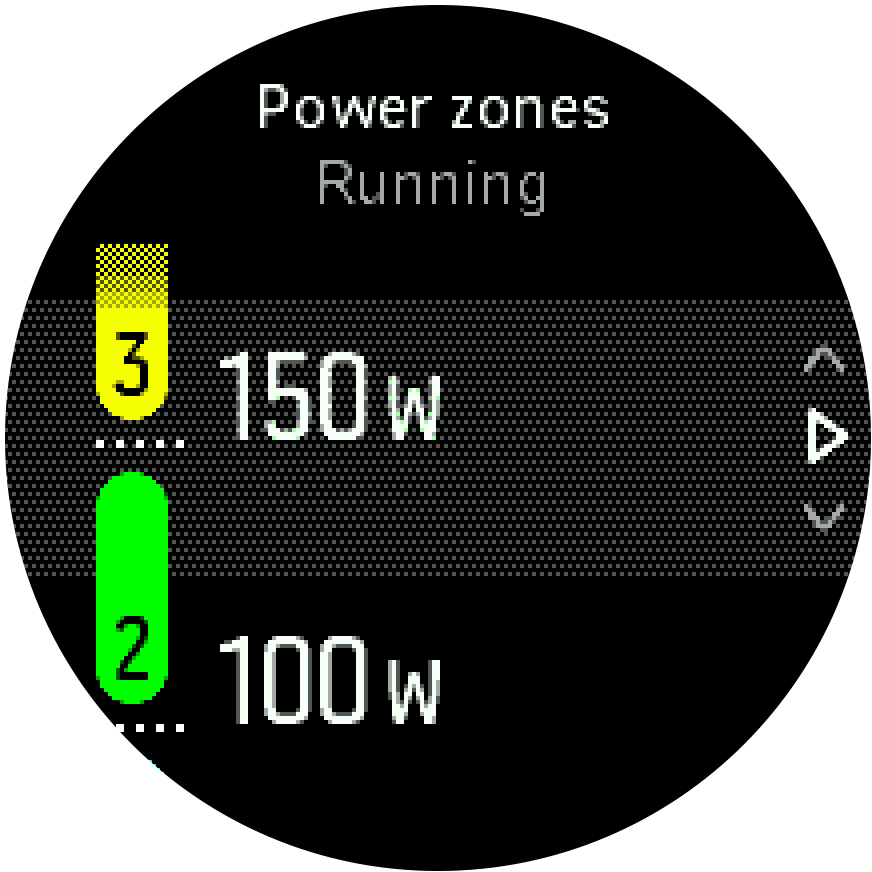
Press the middle button to select the new power value.
- Press and hold the middle button to exit the power zones view.
Using power zones when exercising
You need to have a power pod paired with your watch to be able to use power zones when exercising, see Pairing PODs and sensors.
When you record an exercise (see Recording an exercise), and have selected power as an intensity target (see Using targets when exercising) a power zone gauge, divided into five sections, is viewed. These five sections are shown around the outer edge of the sport mode display. The gauge indicates the power zone you have chosen as an intensity target by lighting up the corresponding section. The small arrow in the gauge indicates where you are within the zone range.

Your watch alerts you when you hit your selected target zone. During your exercise the watch will prompt you to speed up or slow down, if your power is outside the selected target zone.

In the exercise summary, you get a breakdown of how much time you have spent in each zone.